The Nature of Melody
melody shows up in the high range.
Reason:
because the way sound waves operate.
The higher frequencies take a lot shorter time to clear.
melodies play faster notes because those sounds clear quickly and we can hear and enjoy the melody.
The Development of Notes and the Scale
五线谱,每条线之间的frequency /space 是一样的。
重复八度:octave duplication。
很多国家的音乐中,都应用了octave duplication.
west: ABCDEFG,seven notes within the octave.
Indonesia: six notes within the octave.
Example: Ravi Shankar’s raga, 用的乐器 sitar 是一种类似吉他的印度弦乐器
China: five-note within the octave.
Example: 阿炳的《二泉映月》
简介古希腊人处理音乐的方式。
ancient Greeks were very much into mathematics as a way of explaining the world and explaining music in particular.
【这段暂时不懂,待消化书上的内容。】
Major, Minor, and Chromatic Scales in World Music
seven notes within the scale of the major scale
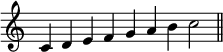
seven notes within the scale of the minor scale
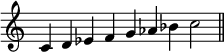
音阶:在八度之内,音的上行和下行的一种固定形式。可以把它想象成一个有八级的梯子,在固定的高和低的两个点之间,由八度形成,可以上或者下这个梯子。
其中,除了BC,EF之间是半级,其他的都是一级。
升号 sharp # VS 降号b flat【相当于键盘上的黑键音】
升调是升半个scale,降调是降半个scale
black notes, can be called sharps or flats. flats are below, take you down a half step, while sharps take you up a half step.
C大调音阶:按钢琴上的白键 CDEFGABC,正好对应着 1-1-1/2-1-1-1-1/2
C小调音阶:按钢琴上的白键CD,DE间的黑键降E,白键FG,GA间的黑键降A,AB间的黑键降B,白键C,正好对应着1-1/2-1-1-1/2-1-1, 即 C D E-flat F G A-flat B-flat C
同理:
A大调音阶:按钢琴上的白键AB,CD间的黑键升C,白键DE,FG间的黑键升F,GA间的黑键升G,白键A。即A B C-sharp D E F-sharp G-sharp A
A小调音阶:白键 ABCDEFGA
tonic note: the primary note
leading tone:pull into the tonic,引出 tonic note,it is always the seventh degree. It’s always a half step.
例子:Luciano Pavarotti 歌唱片段。
Most of our popular music, folk songs and things like that, are written in duple meter and in a major key. Occasionally, you get things written in triple meter and in a minor key — minor key.
example:Gershwin Porgy and Bess,【感觉是duple,minor】
在古典音乐中,小调也是很少的,大部分都是大调。
这里教授举了Beethoven’s Third Symphony 第二乐章 minor部分和 Mozart 的作品片段 。
Major: happy, bright, optimistic.
Minor: somber. 【灰暗,昏暗】
大调和小调的形成历史介绍:
back to sixteenth century, people started writing these things called madrigals, that were tied to texts. And they got in this habit of, every time they had a bright, happy text, they’d set this in one kind of mode or key — a major mode — and every time they had a sad one, they’d set it in minor.
后面教授放了一段犹太人的音乐Traditional Jewish folk music【major 和 minor 之间的界线有点懵逼】
chromatic scale: 半音阶,chromatic 来自希腊语chroma色彩,附加的五个音高的确为音乐增加了色彩。
半音阶会增加紧张和不安。
chromaticism adds tension to music and especially chromaticism that’s pulling up.
Pitch and Rhythm in Beethoven’s Ninth Symphony
这一段完全就是应用前面的所学了。
Beethoven’s Ninth Symphony 第一乐章,前面部分。
乐器:低音提琴,巴松管,小提琴。
texture织体: polyphonic.复式
中间巴松管部分,是countpoint,【没听出来】
低音部分的低音提琴,和声。
后面加入了铜管乐器。
Yale《listening to music》刷课笔记
- Preface
- Lecture 01 Introduction
- Lecture 02 Introduction to Instruments and Musical Genres
- Lecture 03 Rhythm - Fundamentals
- Lecture 04 Rhythmi - Jazz, Pop and Classical
- Lecture 05 Melody - Notes, Scales, Nuts and Bolts
- Lecture 06 Melody - Mozart and Wagner
- Lecture 07 Harmony - Chords and How to Build Them
- Lecture 08 Bass Patterns - Blues and Rock
- Lecture 09 Sonata-Allegro Form - Mozart and Beethoven
- Lecture 10 Sonata-Allegro and Theme and Variations
- Lecture 11 Form - Rondo, Sonata-Allegro and Theme and Variations
- Lecture 12 Guest Conductor - Saybrook Orchestra
- Lecture 13 Fugue - Bach, Bizet and Bernstein
- Lecture 14 Ostinato Form
- Lecture 15 Gregorian Chant and Music in the Sistine Chapel
- Lecture 16 Baroque Music - The Vocal Music of Johann Sebastian Bach
- Lecture 17 Mozart and His Operas
- Lecture 18 Piano Music of Mozart and Beethoven
- Lecture 19 Romantic Opera - Verdi's La Traviata, Bocelli, Pavarotti and Domingo
- Lecture 20 The Colossal Symphony - Beethoven, Berlioz, Mahler and Shostakovich
- Lecture 21 Musical Impressionism and Exoticism - Debussy, Ravel and Monet
- Lecture 22 Modernism and Mahler
- Lecture 23 Review of Musical Style
- Final